Economy, Inflation Breed Caution for Nonresidential Outlook
John Caulfield, Senior Editor, Building Design + Construction
Through September 2022, spending on nonresidential construction was up 9.2 percent, to $883.9 billion, according to preliminary estimates by the Commerce Department’s Bureau of the Census. Sectors hard-hit by the coronavirus pandemic—including lodging, retail/commercial, and even office—were showing signs of life.
See the complete 2023 Annual Report & Forecast.
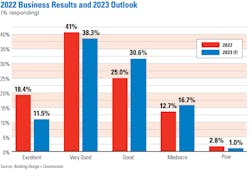
So it makes sense that a recent polling of 212 architects, engineers, contractors, and developer/owners found nearly three-fifths of respondents (59.4 percent) rating 2022 an “excellent” or “good” business year. Only 15.6 percent rated the year “mediocre” or “poor.”
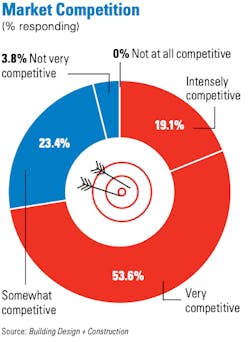
The vast majority of firms, 77.7 percent, rated their overall health “very good” or “good.” Conversely, only 4.7 percent saw their firms’ financial condition as either “weak” or “very weak.” Among the firms polled, 55 percent confirmed that their revenue had increased, and another 20.9 percent said that their revenue was level with last year’s. Gains were achieved despite nearly three-quarters of the firms surveyed characterizing the construction/materials market hobbled by supply-chain snags as “intensely” or “very” competitive.
Euphoria, though, might be short-lived, and firms are tempering their prognoses about the future. Nearly one-quarter (23.4 percent) expect their revenue to be down in 2023, and another 34.4 percent predict a flat year. Competition ranked third, behind general economic conditions and inflation, as the most important concern AEC firms believe they will face next year. Nearly two-thirds (64 percent) anticipate that materials prices will continue to rise in 2023. An even higher number, 71.2 percent, said that they were girding for increases in bid prices for projects.
Our poll also found at least one-fifth of firms are concerned about the availability of capital funding for projects, regulations, cashflow management, and keeping their staffs motivated.
When asked about what business development strategies they planned to deploy next year, more than half (53.4 percent) said that they would hire selectively to burnish their firms’ competitiveness, and 47.1 percent were planning to step up their staff training and education to enhance competitiveness.
Other business strategies these firms are plotting include increasing their marketing and public relations (25.3 percent of firms polled currently don’t use social media, and among those that do LinkedIn is their preferred platform), investing more in technology, and creating new service or business opportunity.
Picking battles, sector by sector
Our survey asked AEC firms to assess their prospects in 18 construction sectors. Sizable percentages (at least 30 percent) were hopeful about business for airports, data centers, government/military buildings, healthcare, industrial/warehouse, multifamily and senior living residential, science + technology, and university. At least 20 percent of respondents saw their prospects as “average” for performing arts centers, hospitality, K-12 education, and sports and recreations. AEC firms placed offices and interior fitouts, religious, and retail/commercial in the “weak” or “very weak” categories.
Here's a closer look at their responses. Keep in mind that these firms aren’t active in every sector, so the numbers providing ratings were smaller than the total in each category. It’s also worth noting that nearly one-third of the AEC firms polled generate between 25 and 74 percent of their annual business from reconstruction projects:
- Healthcare appears to hold out the greatest opportunities for next year. More than 45 percent of respondents rated their prospects in this sector as excellent or good. Multifamily received those ratings from 43.1 percent or AEC firms polled, industrial/warehouse from 39.7 percent, and data centers from 37.8 percent.
- Through September, construction spending in the office sector was up only 0.7 percent, according to Census Bureau estimates. The AEC firms that responded to our survey aren’t anticipating a rebound in this sector any time soon: 41.3 percent rated their prospects weak or very weak. Another 23.5 percent gave the same ratings to office interiors and fitouts.
- Even though Census estimates that the commercial sector (which encompasses retail) was up 22.4 percent through September, our survey’s respondents are still taking a wait-and-see approach, as 33.3 percent saw their prospects in retail next year as weak or very weak.
- Twenty-nine percent of respondents said that their firms don’t build in the retail sector. And even with the uptick in firms that have expanded their practices and services, only around 10 percent of our survey’s respondents see mergers or acquisitions in their immediate futures. Our survey reveals an industry whose firms, in many cases, focus on a limited array of typologies and clients, and leave other sectors to specialists.
- It was not surprising that 53.2 percent of respondent firms aren’t building airports and 41.2 percent aren’t active in the religious sector. Only about half of respondent firms (46.2 percent) engage performing arts center projects, and 44.3 percent keep their distances from data centers. But even some of the broader sectors, notably education, find between 30 and 33 percent of respondent firms absent. Nearly two-fifths aren’t active in science + technology construction, either, and more than two-fifths don’t build in the multifamily sector.